GPS-Based Monitoring System (GMS) Monitoring Procedures
General
The AAMA is responsible for all GMS monitoring activity within the FIRs for which it is responsible. To undertake this monitoring, the AAMA has approved the following Support Contractors to undertake the GMS monitoring activity:
Monitoring Agency for Asia Region (MAAR)
AEROTHAI
102 Ngamduplee Road
Tungmahamek, Sathorn,
Bangkok 10120
Thailand
Ph: +66 2 2878154
Fax: +66 2 287 8155
Email: maar@aerothai.co.th
Availability of EGMU service in the next 5 months: www.aerothai.co.th
Asian Corporate Aviation Management Pty Ltd
1075 West Camp Road
Seletar Airport 797800
Singapore
Contact: Darren Broderick
Ph: +65 6334 0987
After hours ph: +65 8533 8523
24-hour ph: +62 81210696920
Email: darren.broderick@acam.asia or rsvm@acam.asia
Web: www.acam.asia
GMS Description
The GMS is comprised of the equipment and procedures to collect and process three required data elements: GPS data, pressure altitude or Mode C data, and meteorological data. The GPS-based Monitoring Unit (GMU) is used by the GMS service provider to collect data during the monitoring flight. Meteorological data will be obtained by the AAMA without operator involvement.
Monitoring Flights
Monitoring can be conducted on scheduled flights, ferry flights, or monitoring-specific flights. To ensure collection of sufficient position data, the flight must be straight and level at any altitude from FL 290 to FL 410, and should be at least thirty minutes in duration, which can be interrupted by turns. Monitoring can only be conducted in areas within ATS surveillance system (radar/ADS-B) coverage.
GMU Description
The GMU is a portable unit comprised of two Global Positioning System (GPS) receivers and two GPS antennas, temporarily mounted on interior windows. They are usually self contained and battery driven. Some older types of GMUs require a laptop computer and plug in power from the aircraft (draws 2.0 to 4.0 amperes maximum) and accepts multiple types of power standard to aircraft. The GMU can be installed in the aircraft cockpit or cabin, depending upon aircraft type. Installation time is approximately 15 minutes. For most transport aircraft, the GMU is best installed using the aft cockpit windows. The GMS Monitoring Specialist typically occupies a jump seat to monitor GMU performance. GMU installation is transparent to crew operations.
Monitoring Process
Upon receiving airworthiness approval, the operator should contact the AAMA to discuss monitoring options. To start the GMS monitoring process the operator should contact a service provider. The collection of GPS data with the GMU can be accomplished by a GMS Monitoring Specialist or by an operator representative that has received GMU training.
To conduct the monitoring flight, the Monitoring Specialist or operator representative that has received GMS training, will perform the following tasks:
- Submit pre-flight Flight Information Form (FIF) to AAMA and GMS Support Contractor
- Operate GMU
- Submit post-flight FIF to AAMA and GMS Support Contractor
- Submit data files to GMS Support Contractor.
The Monitoring process from the operator’s perspective is illustrated in Figure 1.
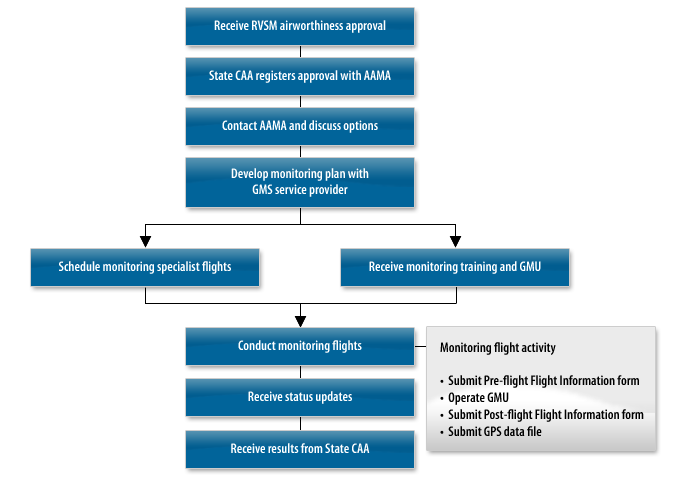
Figure 1. Monitoring process for aircraft operators
Monitoring Post-Flight Information
After completion of the monitoring flight, the GPS data will be processed by the GMS contractor and forwarded to the AAMA who will calculate ASE. Final ASE results should be available from the AAMA within three weeks of the flight. The results will be sent to the State Airworthiness Authority and posted on the AAMA web site.